The great space achievements of humanity
Space exploration is one of the greatest chapters in human history. From our first tentative steps towards the sky to bold plans for colonizing other planets, each milestone represents a monumental leap in technology, science, and philosophy. Let’s delve into the major milestones that have marked our journey into space, highlighting why these moments have been so significant for the evolution of astronautics.
The milestones of space exploration
October 4, 1957: Sputnik 1 ushers in the space age
The launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union was humanity’s first giant leap into space. This small spherical satellite, weighing only 83.6 kilograms, was the first human-made object to orbit Earth. Despite its technological simplicity—it transmitted radio signals detectable on the ground—the success of Sputnik demonstrated the feasibility of exploring outer space. This event ignited the so-called space race between the United States and the Soviet Union, laying the groundwork for future human and satellite missions. It also spurred advancements in rocket technology and satellite communications.
April 12, 1961: Yuri Gagarin becomes the first human in space
Just four years after Sputnik’s launch, the Soviet Union achieved another extraordinary milestone. Yuri Gagarin, aboard the Vostok 1 capsule, completed a full orbit around Earth in approximately 108 minutes, becoming the first human to leave Earth’s atmosphere. This moment was not only a technical triumph but also a symbolic achievement of immense magnitude. It demonstrated that humans could survive the harsh conditions of space and opened the door to an era of manned exploration. Gagarin’s heroism inspired millions, fueling collective imagination about humanity’s future in space.
July 20, 1969: Apollo 11 and the moon landing
“One small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” With these words, Neil Armstrong delivered one of history’s most iconic phrases as he became the first human to walk on the Moon. The Apollo 11 mission wasn’t just a technical achievement but also a symbolic victory in the space race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Landing two men on the Moon and bringing them back safely required groundbreaking technological advancements, such as the Eagle lunar module and the powerful Saturn V rocket. This event solidified America’s technological dominance and inaugurated a new era of lunar exploration, showcasing humanity’s ability to explore other celestial bodies.
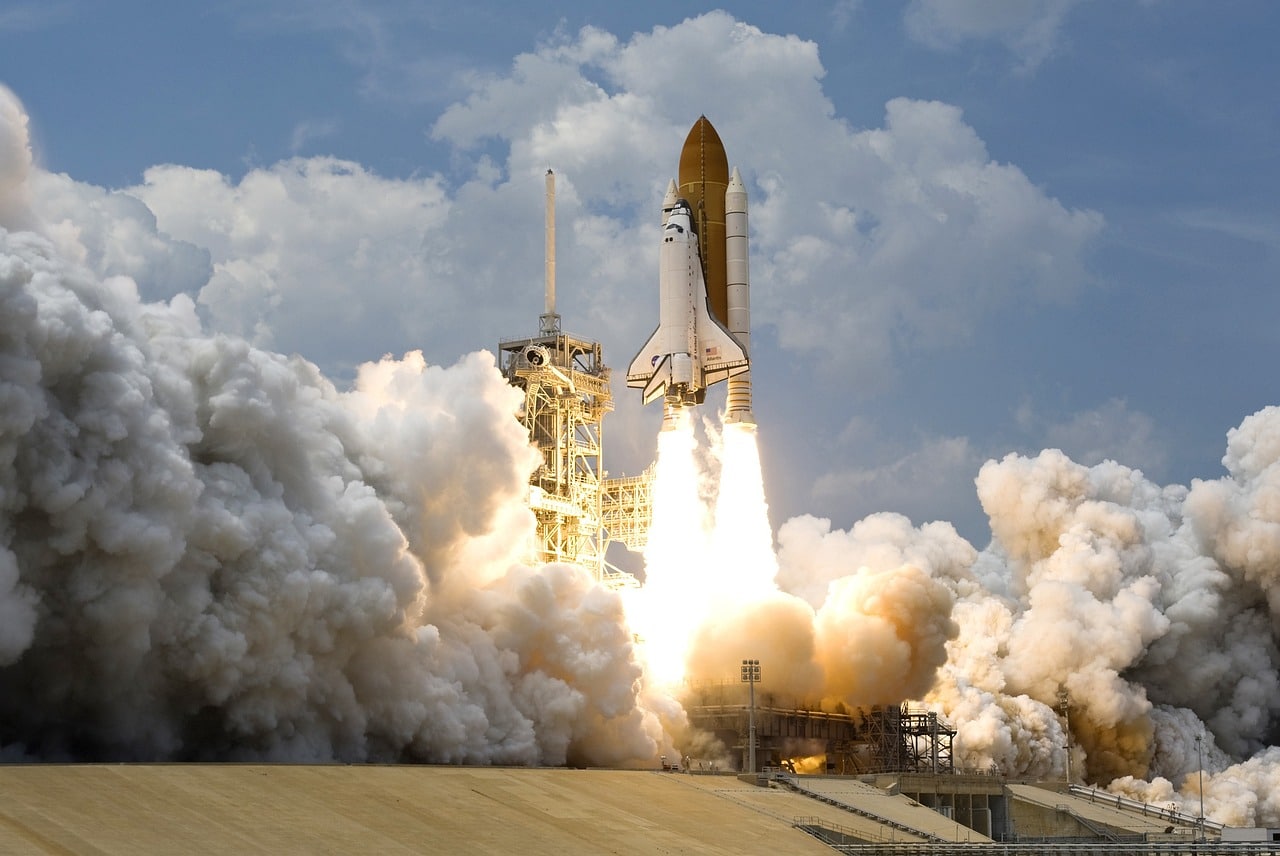
April 12, 1981: space shuttle Columbia and reusability
The launch of the Space Shuttle Columbia introduced a revolutionary concept: reusable spacecraft. Unlike previous missions, where rockets and capsules were lost or destroyed, the Shuttle was a reusable system that lowered mission costs and increased frequency. The Shuttle became a key tool for scientific experiments, satellite deployment, and the construction of the International Space Station. Although the program faced tragic losses—such as the Challenger in 1986 and the Columbia in 2003—it remains a symbol of humanity’s ability to innovate and adapt in the face of challenges.
November 20, 1998: the birth of the International Space Station (ISS)
The International Space Station is perhaps the greatest example of international cooperation in the history of space exploration. The first module, Zarya, was launched in 1998, marking the beginning of a joint project between NASA, Roscosmos, ESA (European Space Agency), JAXA (Japan), and other space agencies. The ISS has become an orbiting laboratory where astronauts from around the world conduct microgravity experiments, study the effects of space on the human body, and test technologies for future missions to Mars. The station is not only a symbol of scientific progress but also of diplomacy and global collaboration.
The SpaceX incident of january 2025
On January 16, 2025, SpaceX faced one of the most challenging moments in its recent history. During the seventh test flight of the Starship rocket, the vehicle suffered a critical failure, exploding eight minutes after liftoff. The incident was attributed to a propellant leak that triggered an internal fire, causing pressure to exceed the spacecraft’s structural limits. Despite the setback, no injuries were reported.
This incident highlights the inherent risks of technological innovation in space exploration. SpaceX, however, remains a leader in revolutionizing space access, thanks to projects like the reusable Falcon rockets and the Starlink satellite constellation. While the failure represents a temporary step back, it has provided valuable lessons for improving safety protocols in future missions.
Space exploration has never been deterred by challenges. Looking to the future, we stand on the brink of a new era. The coming decades will see humanity return to the Moon through the Artemis program and possibly land on Mars by the mid-21st century.
The involvement of private players such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and other companies has accelerated innovation and reduced mission costs. Additionally, increasing attention to sustainability in space is driving creative solutions to address space debris and ensure the responsible use of Earth’s orbit.
In the distant future, humanity might witness the construction of self-sustaining colonies on other planets, using extraterrestrial resources to survive and expand civilization. While obstacles remain, the history of space exploration shows that humanity is capable of overcoming any barrier, driven by curiosity and the desire to explore the unknown.
In conclusion, as we celebrate past achievements, we must continue to look to the stars with hope and determination, knowing that humanity’s journey into space has only just begun.